Portello an integrated urban development project in Milan is the fifth article on projects from practice. The development area defined as Portello Nord, is the northern part of a large former Alfa Romeo Industrial plan dismantled in 1982. It is located in Milan’s northwestern quadrant, close to the outer ring road.
A dynamic part of the region, adjacent to the new Fair District, the Expo 2015 site, and City Life, an urban project to redevelop the former Milan Fair site. The 1980 General Plan designated the whole of the former car factory for industrial use, but with the rapid changes in the economic context and the abandonment of urban factories, the projected land-use designation was abandoned. Meanwhile, the need to develop the neighboring Milan Fair site was at the heart of the process of rethinking the area’s land use. After several changes, the decision was taken in 1994 utilizing a framework agreement to dedicate the southern part of the site to the new exhibition buildings and the northern part to a multifunctional neighborhood see Figure 1,2.
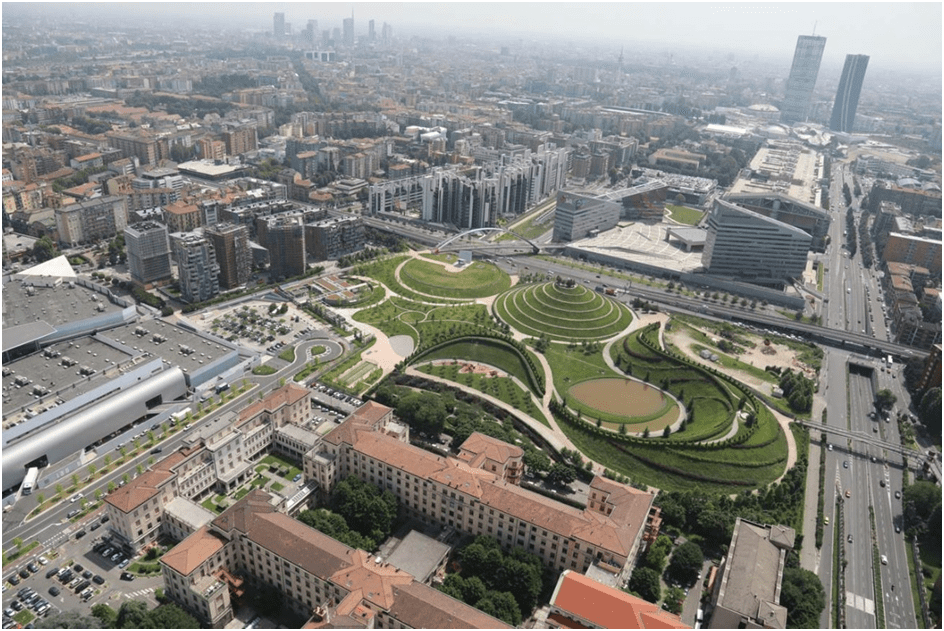
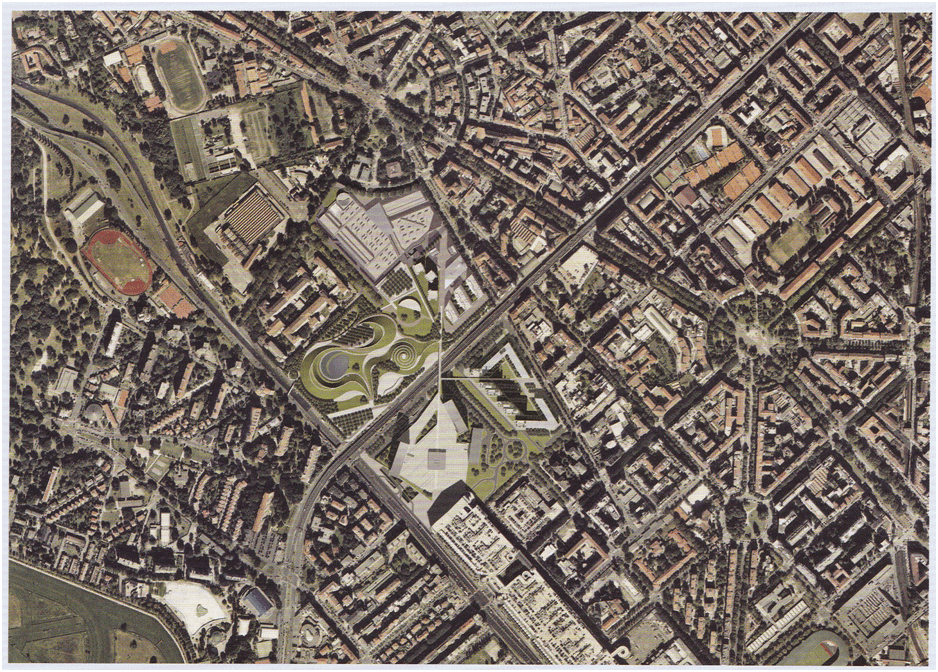

The urban development master plan is a site of a rectangle shape of about 26.5 ha, set along the main northwestern road axis and divided into two more-or-less equal parts by the ring road. Surrounded on two sides by residential areas: to the west a long network of 20th century buildings. To the east, modernist parallel building blocks. On the other side a large roundabout with heavy traffic and a fair extension pavilion.
The objectives of this development are to redevelop a former industrial site of car manufacturing, Removal of the heavy traffic passing the site and the extra coming from the new development from the core area, replanning the development land use to fit sustainable methods and approaches, introduce a new green space to serve the existing surrounding development, creating a matrix of green spaces, increasing pedestrian links in the development and connecting them to the adjacent ones.
The master plan in Figure 3 shows the five sectors of the urban development of Portello. The OT8 slopped hill landscape (1) of the central park was developed to connect the development with other parts, green space, pedestrians, and bridges by a sequence of piazzas.
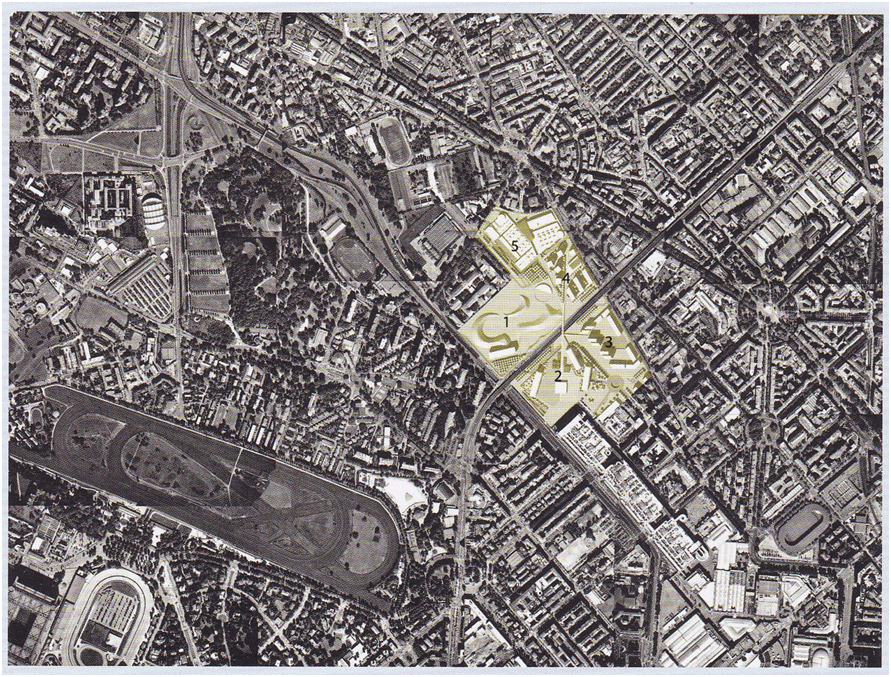
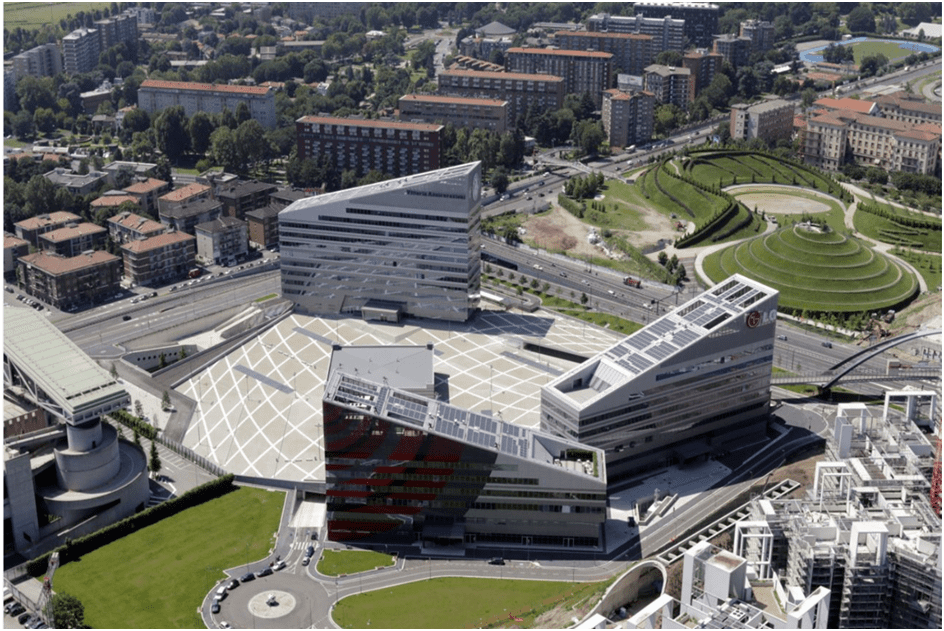
The slopping square (2) inspired by the OT8 blocks has a covered entrance to the below retail and restaurants underground with parking see Figure 4. The three office blocks’ elegant architecture emphasize the direction of movement to the bridge on top of the ring road connecting at the end to the five middle-size retail center (5) with a sail piazza that became a landmark of the area see Figure 5.
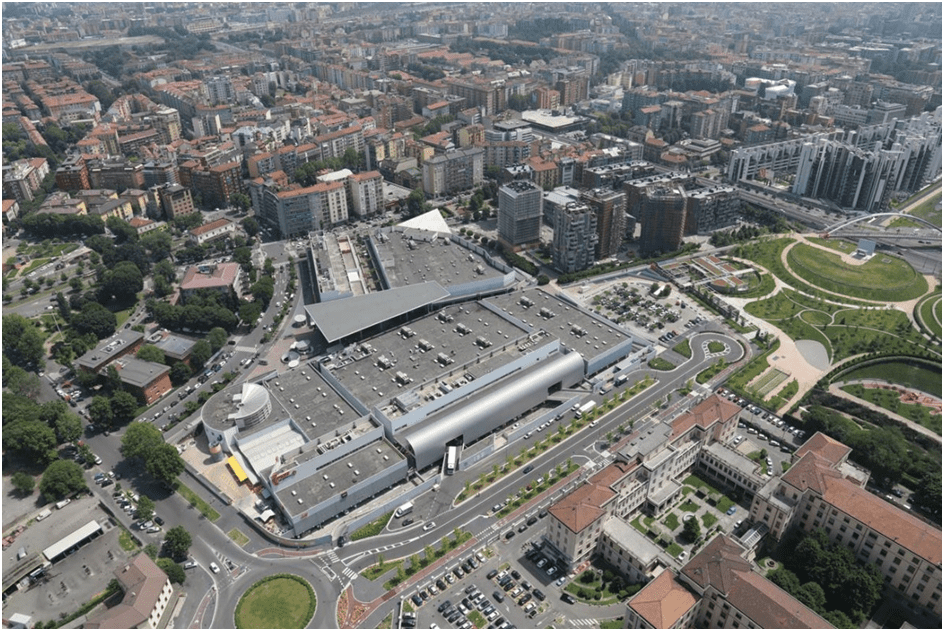


The porous residential area layout (4) is divided by pedestrian routes leading to different locations and connecting old and new urban fabric. The building is oriented to connect visually by a focal point of the landscape. The layout kept the former Alfa Romeo canteen as a memorial from the past industrial development.
The south side of the development area (3) includes two typologies a continuous tall building on the premier road, and six fifteen-story towers facing the pedestrian core and the park. In this area, the urban density is higher than the other areas as an approach to creating a diversity of massing and densities.
The Portello urban development project was accomplished and designed by various firms from European countries to arrive at its successful end achieving its objectives, goals, and urban sustainable development.
One can find in conducting a more focused analysis of this urban development project that it’s the new, modern, look of the old-style Roman cities that consist of multiple open areas of piazzas surrounded by public places and buildings. An innovative way to connect the urban fabric is by flying bridges, pathways, green space, and open space. A homogenous space, greenery, pathways, and building layout in different scales make this on-ground painting. The urban development was planned for completion in 2012.
Be First to Comment