Design Manager Design Management Plan Key Functions is the fourth article of a series of articles about design management in architecture practice. I have discussed in the previous articles what is design management, who is the design manager in practice, and what a project or firm design management plan. In this article, I am going to discuss that, in practice, before building a design management plan I am going to stand on the key functions of a design management plan in practice before going through the process of building and writing a management plan for a firm and a project.
The first step of every project in practice is the announcement of an award of a project through direct assignment from a client or through a bidding process for consultancy service. The second step is the design manager meeting with the client.
Client relations is one of the most important key functions of a design management plan that should include the method to handle client relations. Clients are categorized by their specialization whether they are private sector and that have a lot of sub-categories, I will come to that in later articles, or public sector clients. The fact is that a design manager should understand and study the client in terms of his knowledge in the field of architecture and involvement in construction. How is the client involved or motivated to participate in the development of the project design or rely totally on the consultant to do so? Understanding his concerns about the project design and other phases of the process and responding positively. Another important factor in practice is what type of expertise, knowledge, and skills are required to gain his cooperation, understanding, approvals, and motivation to push the project design forward. What is the best way to communicate in this manner with him to gain his positive input?
Human resources management is one of the main functions of a firm or consultancy company. One of the major success factors in running a consultancy firm is having a powerful human resource professional or team. The five core areas of human resources are recruiting and staffing, compensation and benefits, training and development, talent management, and safety and compliance.
A design manager in the design management plan identifies and intersects with operations and works with the human resource team in their areas of concern when building a design management plan. The areas of intersections are what type of staff is required for the architecture team in terms of expertise, knowledge, academic qualifications, training and development acquired, skills, and certificates gained. On the other hand, continuously updating the internal agenda for staff training and development where serves the company’s development plans and goals. For example, in a European firm I worked with there was a continuous focus on authority requirements of staff expertise, knowledge, and skills. Authorities requested all consultancy firms to upgrade all their application for approval by submitting drawings prepared by Revit software. This software includes BIM 360 to facilitate the construction work but not all consultancy firms are applying this procedure.
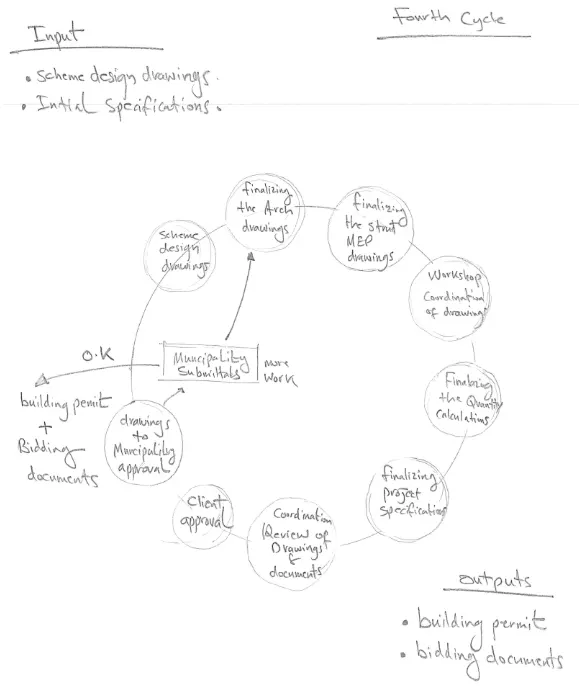
Design process analysis, assessment, and improvement is another key function of the design management plan in practice. In analyzing the project program and component a full process of the design is analyzed and assessed. The design manager lays out the structure flow of the architectural design activities. The architectural design process is divided into five stages. Every stage requires a specific type of staff, expertise, knowledge, and skills. For example, in the concept design phase, a concept senior architect is required to produce innovative designs, prepare or coordinate presentation work, and attend and talk in presentations with clients. In the last phase of the design process, other types of senior-level architects and engineers are required who have expertise in the construction process, systems, building systems, and building specifications and construction drawings requirements. A register and record of the performance of every project regardless of the size of the areas of defects and the improvements required for staff, processes, and software that could improve the efficiency of work and production. This register is an identification for future work of who, and what to include in coming projects. Another important factor is to include design methods that are used in practice and that are feasible to use and fit the project design and team context. Every method needs a special type of staff that possesses knowledge, expertise, skills, and understanding of how to apply it in practice to maximize efficiency and increase project revenue. See Figure 1, the last architectural design phase in practice.
Communication and interpersonal behavior function has a great effect in increasing the performance of staff and firm work efficiency and revenue. When a design manager writes A communication plan identify the consultancy firm’s hierarchy of communication. For example, a junior-level draughtsman should not email or communicate the director level of internal personal problems but to the HR department. An increment of salary request is submitted to the HR department rather than the director-level staff. Other than that consultancy firms have internal systems or use software like SharePoint to communicate many matters related directly to the project design phases. Other consultancy firms conduct communication verbally when it is required specified by the design manager. For example registry and communicating internal meetings for projects, design review meetings, project design reports, and project design progress reports.
Internal behavior and well-being of staff environment are documented by some consultancy firms and handed over to staff on employment. These specific behavioral attitudes are occasionally informed to staff in meetings. One of the major factors that consultancy firms focus on is the performance review due to its direct relation to interpersonal behavior and skills that are used in staff development plans. A staff performance review will benefit both staff and consultancy firms in identifying staff competence like understanding, adjusting, developing, and implementing. These key criteria of interpersonal skills are the gauge and measure of valuable staff members.
Skills/experience evaluation and development is an important function due to its direct link to the architectural design process and production. Every staff member employed goes through an identification of skills/expertise evaluation initially at the time of employment where a design manager takes a direct role in it. But in later stages, many show a lack of expertise and knowledge in some critical areas like the direct relationship between the structural system and the architecture concept preparation and how it contributes to innovative work production. Lack of this critical expertise leads to many adjustments in the concept design in later stages that affect revenue and decrease client satisfaction. Every staff member after several years of work in the consultancy firm finds a register of the areas of required development he needs to conduct. Consultancy firms provide some assistance in some areas by providing training for subjects like project management because it is only provided and requires a couple of days. Improvement and development in areas like software usage like BIM 360 require more time, like months, that is left to the staff member to decide to acquire in the future.
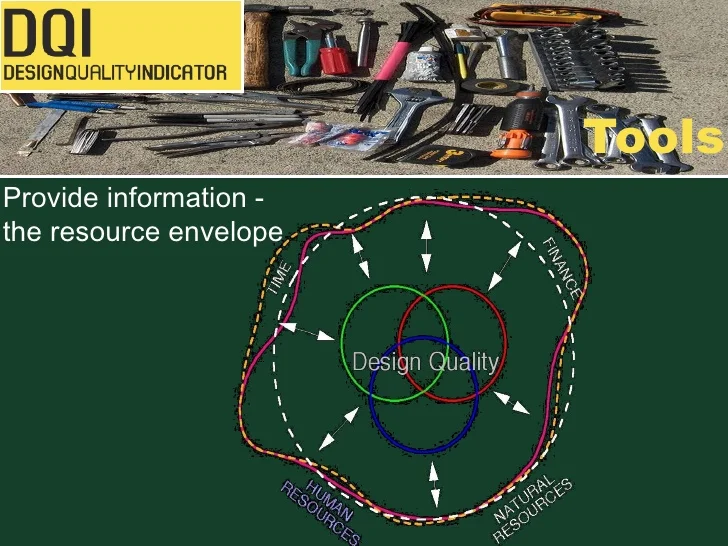
Design production assessment and improvement function is conducted by the design team senior level, supervised by the design manager, to increase efficiency and contribute to project revenue. Consultancy firms, though it is personal views and taste, rely on the senior level to judge production what we call in practice expert judgment. Some consultancy firms build their judgment criteria of assessment of production work and others rely on software or methods built by others like firms and individuals like DQI which is used in the facility management and construction field. Though this is not very useful in design production assessment it is a reference for some consultancy firms. If you are looking to build an indicator of assessment in architecture you can download my book that describes my method of building an indicator when you subscribe to my newsletter. Upon identifying and having an indicator to gauge production areas of defects and areas that need improvement are identified for further action. See Figure 2, the DQI method of assessment.
Authorities’ liaison and coordination is one of the most important functions in the Middle East architecture consultancy work. Consultants here define a specific person who has sufficient knowledge and expertise of the applications, coordination, approval process and requirements, and ways to facilitate the project planning and permit approval which has a direct connection to the design manager. In one country like the UAE, different cities have their specific rules and regulations that are different than other cities. The approval process varies from city to city and in some cities consumes more time than the architectural design time limit allocated for a project. Cites combine the planning and building permit in one organization like a municipality but in other cities, every part of the approval process is located in different departments like planning, municipality, water and electricity, drainage and infrastructure, and security approvals.
[…] Design Manager: Design management plan key functions. […]
[…] Design Manager: Design management plan key functions. […]
[…] Design Manager: Design management plan key functions. […]